Importance of Peer Review in Academic Publishing: Ensuring Research Quality and Credibility
Unlock the importance of peer review in academic publishing. Learn how to validate research, build credibility, and get your manuscript published faster

Jacqueline
A Machine Learning Research Paper is a structured study that presents original algorithms, experiments, and evaluations of models designed to solve real-world problems. Publishing one isn’t easy reviewers scrutinize your methodology, check dataset credibility, and test whether your experiments are truly reproducible. Modern foundation models like ChatGPT and Gemini represent key milestones in ML evolution, helping researchers draft, debug, summarize, and accelerate experiments.
The impact of these papers and tools extends globally, powering technologies in daily life like recommendation systems and voice assistants, improving business decision-making, advancing healthcare through disease detection and drug discovery, and driving innovation across industries. This guide walks you through the full technical workflow, evaluation strategies, publication tips, and rare insights from reviewers to help your paper succeed.
A Machine Learning Research Paper formally documents original technical contributions to the field and demonstrates measurable progress over existing methods. Machine learning research papers should not be used only for sharing results, but rather for proof that can be verified by readers. Important points related to research papers in machine learning involve:
Presents novel algorithms, architectures, or improvements in methodology. These might be related to optimization algorithms, novel loss functions, or innovative architectures that will solve problems that had not been solved or were solved inefficiently. A contribution must certainly advance the state of the art.
The ability of the experiments should be fully reproducible. This means the datasets are shared, or the exact source and processing directions are mentioned, code, model parameters, and specifications.
The reproducibility aspects of the experiments often come under scrutiny, and gaps within the details result in dismissal of the paper, despite good results.
The results attained by models must be statistically proven using relevant metrics like accuracy, F1-score, ROC AUC, and MSE, among others, based on the task.It is expected that results be presented based on various runs, compared to baselines, and significance statements. It is evidence that separates these researchers from just hypotheses.
Unlike review papers, a deep learning research paper will be concentrated on experimental results rather than a collection of information about prior work.
It needs to present new views, be innovative, and show evidence that can be used for a conclusion.
The best-quality papers clearly describe the datasets that were considered and their processing procedures. The reviewers also scrutinize whether datasets exhibit bias, imbalance, or leakage problems. The reporting allows both for the reproducibility and the ethical violation requirements that nowadays characterize high-quality machine learning research.
Training a machine learning model is an iterative process that follows three key steps: First, the model makes predictions on the input data using its current parameters. Next, it calculates the loss, which measures how far its predictions are from the actual results. Finally, the model performs parameter updates, adjusting its internal weights to reduce the loss. This cycle repeats multiple times until the model achieves the desired level of accuracy.
After training, the model is tested on unseen data to check its ability to generalize. Generalization ensures the model works beyond the training data and avoids overfitting, making it reliable for real-world applications like recommendation systems and healthcare predictions.
The Machine Learning Research Paper’s claims are held under the microscope for strict technical evaluation because the claims need to be reproducible, verifiable, and able to be defended when peer-reviewed. The reviewers check for several important factors:
Does the paper introduce a genuinely new algorithm, model architecture, or methodological improvement that advances the state of the art? Reviewers expect a clear justification of why the approach is innovative compared to prior work.
Are the datasets employed relevant to the research task, well-documented, and unbiased or free of data leakage? It's important to be transparent about preprocessing, data augmentation, and splitting for training, validation, and test sets to promote credibility in the work.
It helps to see that other people can produce similar results by running their code, hyperparameters, and environments. Non-reproducibility leads to many rejections when results seem to be excellent.
Careful selection of evaluation metrics that closely correspond with the claims being made in the research work. The reviewers examine statistical significance, comparison with a base case, and whether there is a strong connection with the contributions proposed.
Many papers will fail early because the methodology is unclear, the data set is not well described, and the experiments cannot be reproduced. Even good technical results will not get accepted if the process cannot be reproduced.
A well-structured Machine Learning Research Paper ensures clarity, reproducibility, and meets the scrutiny of expert reviewers. Each section serves a distinct purpose
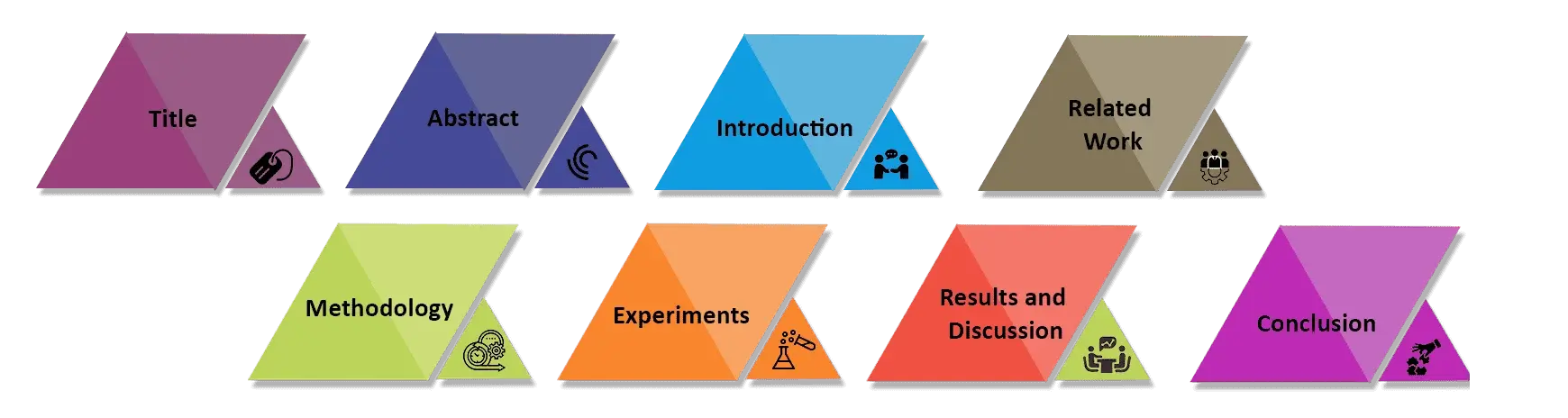
Title: Concise and problem-specific; signals relevance immediately.
Abstract: Problem → method → dataset → results → novelty; convinces reviewers to read on.
Introduction: Define the research gap and motivation; show why the work matters.
Related Work: Compare with prior methods; highlight improvements and differences.
Methodology: Detail algorithm, architecture, and hyperparameters; ensure reproducibility.
Experiments: Describe dataset splits, preprocessing, and baselines; include reproducibility details.
Results and Discussion: Present metrics, significance, and analysis; discuss implications and limitations.
Conclusion: Summarize contributions, limitations, and future work; reinforce novelty and impact.
By framing each section with reviewer expectations in mind, your Machine Learning Research Paper becomes not only clear and organized but also maximizes acceptance potential.
Impact on Acceptance: Dataset choice affects paper acceptance in terms of reviewer perception.
Cleaning: Remove duplicates, address missing values, and eliminate noise from the dataset.
Normalization: Scale the features to enable fair convergence of models.
Augmentation: Applying transformations that can increase the diversity of the dataset.
Bias & Imbalance Check: The class distribution for potential biases and the fairness of the data is evaluated.
Reproducibility: All preprocessing steps should be recorded so that results can be verified in other experiments
Algorithm and model design determine the technical strength of a Machine Learning Research Paper and are a key focus during peer review. Clear architectural documentation and justified design choices signal rigor, reproducibility, and meaningful innovation.
Describe clearly the model layers, the number of parameters, and optimization methods.
For architecture thesis projects, include diagrams or tables that illustrate layer connections and data flow.
Instead of stating what was used, explain why specific learning rates, batch sizes, or regularization values were chosen.
Justification of model depth and size with respect to the dataset scale in order to avoid any concerns regarding overfitting.
The practice of comparing models with either standard or simpler versions for the determination of meaningful performance gains.
Abolish components or alter them to demonstrate which pieces of the model drive improvements.
Reviewers look for logical design decisions backed by experimental evidence and not trial-and-error tuning.
The experimentation process is central to validating claims in a Machine Learning Research Paper and is closely examined during peer review. Clear, systematic reporting ensures results are reproducible, credible, and scientifically sound.
Clear Experiment Reporting: A clear description should be given for each stage of the experiment to make the process clear in the Machine Learning Research Paper.
Number of Runs: This refers to the number of times the experiments were done to cover the variations of results.
Random Seeds: List the random seed values used for the purpose of reproducing results.
Hardware and Compute Infrastructure: GPUs, CPUs, memory, as well as the software frameworks used in experiments.
Functionality of Reproducible Code: Sharing complete code on platforms like GitHub or supplementary material with proper usage descriptions.
Reviewer Insight: One of the major issues with Machine Learning papers being rejected for Machine Learning conferences and journals relates to issues of reproducing results, even where the metrics are very good.
Evaluation metrics are essentially an imperative part of Machine Learning Research Papers in determining model performances as well as in attempting claims in the paper by ensuring their veracity through intense analyses based upon carefully chosen metrics.
Select evaluation metrics based on the type of problem. For classification tasks: accuracy, F1 score, ROC AUC; for regression tasks: mean squared error or other error-centric measures
Include calibration, robustness, and/or fairness metrics if appropriate to give more perspective regarding the results of the model.
Determine if the gains found are significant in nature rather than due to random variations.
Reviewers verify if the selected metrics accurately match the proposed advantages; otherwise, the proposed advantages may be rejected, although the result is technically high-quality.
Ethics now play an essential part of modern machine learning research. It is expected from a Machine Learning Research Paper to describe the strategy adopted to mitigate the bias in the model, ensure fairness, and privacy of data, especially when models are applied in real-world scenarios. Clearly depicting these steps makes the research more trustworthy and transparent.
It pays to know that, other than technical strength, ethical considerations can create either the best or worst chances of being published. Often, reviewers reject technically strong papers because the authors failed to discuss issues of bias, fairness, and privacy risks. This not only increases your credibility but also satisfies the standards that top ML journals expect.
Non-reproducible results: Experiments cannot be reproduced due to code being missing, settings not being clear, or preprocessing not being documented.
Insufficient dataset documentation: Most rejections occur due to a lack of description of sources, splits of data, or pre-processing.
Poor baseline comparison: Claims of improvement are not credible without comparisons to standard or simpler models.
Misaligned evaluation metrics: Metrics that are not aligned with the problem or claimed contributions hurt reviewer confidence.
Lack of novelty or unclear contribution: Papers that do not make a clear contribution to the advancement of the field, or where the relationship to prior work is not obvious, are often rejected.
Research paper writing services, or review by our experts within, can help overcome the possibility of rejection. Peer review involves checking the program codes, data, and methodology for authenticity prior to publication in a particular journal. Peers are easily impressed with manuscripts that are checked by experts, thus publishable articles are easily attainable.
Ensure datasets are fully documented and reproducible.
Share the code with clear instructions and confirm it runs correctly.
Explain model architectures and hyperparameters in detail.
Justify all evaluation metrics used and ensure they align with claims.
Clearly state contributions, novelty, and limitations of your work.
A good Machine Learning Research Paper is original, technically excellent, and transparent. Being transparent in detailing your data, models, experiments, and results in your paper can go a long way in making your paper reproducible, thereby winning the acceptance of the reviewers. By following the right methodological approach, using appropriate metrics, and taking into account the right ethical issues, researchers can increase the chances of acceptance of their paper in the field.
Unlock the importance of peer review in academic publishing. Learn how to validate research, build credibility, and get your manuscript published faster
Master the top methods of primary data collection in research methodology. Learn to use surveys, interviews, and experiments to gather original, high-quality data.
Don’t write your methodology without reading this. Learn why purposive sampling is essential for case studies and how to define your inclusion criteria. Url:purposive-sampling
Master the chapterization of thesis to ensure logical flow. Learn the standard academic framework for organizing research into a professional, approved document.
A practical guide to sentiment analysis research papers covering methodologies, datasets, evaluation metrics, research gaps, and publication strategies.
Master data analysis for research papers. Learn quantitative and qualitative methods, cleaning, and reporting standards to ensure your study meets journal rigour.